Last review: December, 2025
Banobras offers interested parties information on the sector in Mexico with data from various sources in order to provide knowledge on the subject and useful elements for decision-making at the sectoral level. The content presented does not reflect the position of Banobras.
DOF: AGREEMENT issuing the General Cybersecurity Policy for the Federal Public Administration. (Dec. 17, 2025). Consult
Current status
The Telecommunications and Broadcasting (TyR) sector is undergoing a global transformation toward a cross-cutting dimension for the development and provision of digital services and content in society. At the same time, this sector serves as a generator of digital inclusion and the closure of the social gap, under the broad concept of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). Currently, most daily activities involve the use of telecommunications products or services: radio, television, telephone, or the internet.
The TyR sector encompasses multiple activities, including, first and foremost, the operation of public telecommunications networks, as well as the provision of public telecommunications and broadcasting services (SPTyR). These public telecommunications networks, in turn, rely on various inputs, including:[1]
- Radio spectrum
- Passive infrastructure and cabling
- Passive tower infrastructure
- Active infrastructure equipment and services for TyR networks and user terminals
According to the Telecommunications and Broadcasting Law, it refers to all emission, transmission, or reception of signs, signals, data, writings, images, voice, sounds, or information of any kind that is carried out through wires, radio electricity, optical media, physical means, or other electromagnetic systems, excluding broadcasting.

Public Shared Telecommunications Network
The shared telecommunications network refers to when telecommunications marketing companies and network operators share their infrastructure, aiming to promote greater competition in the telecommunications sector. It offers wholesale services to facilitate the development of regional and national concessionaires and marketers, achieving greater coverage and quality, at competitive prices for telecommunications services to the general population.[2]
Fixed telecommunications services[3]
These include the distribution of fixed services to homes; total access numbers/lines; market share and concentration; and the number of access lines per 100 households nationwide.
- Television: In 2000, there were 14 service accesses per 100 households. By December 2023, this number had increased to 61.
- Fixed internet: 58.4% of service accesses were through fiber optic. 89.4% of SMEs subscribe to fixed internet service.
- Fixed telephony: The number of fixed telephony lines increased from 25.0 million in 2021 to 26.5 million in 2022. This represented an annual growth rate of 8.6%, which is an increase of a little more than 1.5 million lines in one year.
Mobile telecommunications services[4]
These include the distribution of radio spectrum by frequency band and by operator; the use of mobile services by the population; the total number of lines; market share and concentration; the number of lines per 100 inhabitants nationwide and by federal entity; and the traffic of mobile phone services and internet access.
- In 2023, there were over 144.7 million mobile phone service lines nationwide, representing a 7.5% increase compared to December 2021.
- In the mobile internet access service, there were 96 lines per 100 inhabitants nationwide, reflecting a growth of 229.5% since 2013.
- Mobile internet access lines grew by 5.1% from 2022 to 2023, increasing from 109.5 million lines in 2021 to 126.06 million lines in 2023.
Economic indicators in Mexico[5]
- In 2022, the revenues of telecommunications sector companies totaled 603 billion pesos.
- In 2023, the GDP of the telecommunications and broadcasting sectors experienced an annual growth of 6.8%.
- 86% of jobs were in the telecommunications sector, while 14% were in broadcasting.
- In June 2024, foreign direct investment (FDI) in the telecommunications and broadcasting sectors was $169.1 million, representing 1.5% of national FDI.
In Latin America, according to data from GlobalData, the mobile communications market generated revenues of $56.8 billion in 2021. In Mexico, mobile phone service lines showed a compound annual growth rate of 2.72% between 2013 and 2022. In 2023, telecommunications operators reported revenues of over $28.8 billion.[6]
For more information about Mexico in the international context, please consult the following link.
[1] Instituto Federal de Telecomunicaciones, Strategy IFT 2020-2025
[2]PROFECO, “What you should know about telecommunication services”
[3] Instituto Federal de Telecomunicaciones, Statistical Yearbook 2023
[4] Ibid
[5] Ibid
[6] Instituto Federal de Telecomunicaciones, Forecast of Telecommunication Services 2023-2024
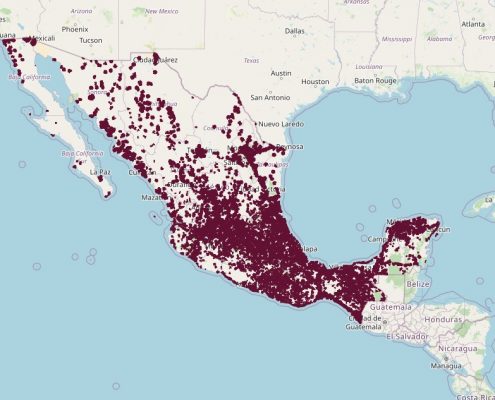
PROMTEL makes available to the public the spatial data viewer where you can see the coverage maps of the Shared Network showing the project’s coverage progress.
Institutional Arrangement
In terms of infrastructure, Mexico has a defined strategy that offers investors medium and long-term visibility regarding the development of projects, through a series of plans and programs of national and sectorial scope. To access the information, please consult the following documents:
Sectoral Program of the Agency for Digital Transformation and Telecommunications 2025-2030.
National Radio Spectrum Program 2022-2024
Organizational Structure
Description of the hierarchy and roles of the different entities and actors involved in the sector, including how the different institutions and agencies coordinate and collaborate.
The Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency is a Federal Government entity responsible for the sector, ensuring compliance with telecommunications and technological development regulations. Its mission is to build a model of technological autonomy by unifying capabilities, generating public savings, and creating public value.
Its work is guided by the following principles:
- What exists in person can exist digitally.
- Minimize the regulatory burden on individuals and businesses.
- Savings, zero corruption, and interconnected public systems.
- A single assistance number: all issues, every day, at any time.
- Data intelligence to strengthen public sector capabilities.
- Technological autonomy and information security.
- The Internet is a right.
The Telecommunications Regulatory Commission is a decentralized administrative body of the Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency, with technical, operational, and managerial independence. Its purpose is to ensure the efficient development of telecommunications and broadcasting in Mexico.
The National Commission for Regulatory Improvement (CONAMER) is a decentralized administrative body under the Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency, with technical and operational autonomy. Its objective is to promote the improvement of regulations and the simplification of procedures and services, as well as transparency in their development and implementation. CONAMER ensures that regulations generate benefits that outweigh their costs, maximizing societal benefits.
Decentralized public entity in charge of using space science and technology to meet the needs of the Mexican population and generate high value-added jobs, promoting innovation and development of the space sector; contributing to the competitiveness and positioning of Mexico in the international community, in the peaceful, efficient and responsible use of space.
Decentralized public entity in charge of contributing to improve the coverage and quality of Internet and telephony services, supervising the installation of the Shared Network and promoting investments for telecommunications infrastructure deployment projects.
Institutional Program of the Organism Promoter of Investments in Telecommunications 2025-2030.
A Federal Government Public Research Center contributing to Mexico’s Digital Transformation through research, innovation, academic training, and the development of ICT products and services. Its impact spans both the public and private sectors, paving the way toward a modern Mexico characterized by digital inclusion.
CFE Telecommunications and Internet for All is a productive subsidiary of the CFE, with its own legal personality and assets, that provides telecommunications services. Its goal is to install wireless internet across the country—on highways, in public squares, health centers, hospitals, schools, and community spaces—to help combat marginalization, integrate underserved regions into productive activities, and close the digital divide by ensuring equal access to information and communication technologies, especially for people in areas currently disconnected from telecommunications.
Legal system
The compilation of international treaties, laws, regulations, decrees, agreements and federal, state and municipal provisions shown here are for informational purposes and for ease of reference:
Law on Telecommunications and Broadcasting
SICT
Public Works and Related Services Law

Public Shared Telecommunications Network
Investment Cycle
The following section provides an overview of the project development process from initial planning to final execution.
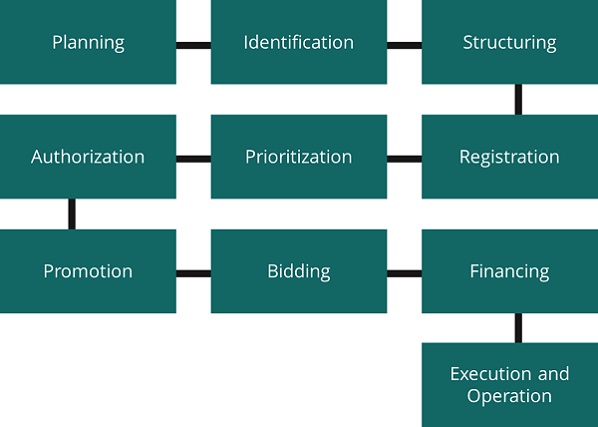
Planning
Based on the objectives and strategies defined in the National Development Plan, the Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency develops short-, medium-, and long-term sectoral programs for the development of communications-related infrastructure.
Identification
The Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency identifies the needs of the sector to carry out communications infrastructure projects to be developed.
Structuring
The Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency prepares, on its own or with the support of external consultants, the studies and analyses necessary for the development of telecommunications projects.
Registration
The Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency sends to the SHCP’s Investment Unit the request for registration in the portfolio of highway projects that require federal public resources from the Federal Expenditure Budget (PEF).
Prioritization
Projects requiring federal budgetary resources must be analyzed by the Comisión Intersecretarial de Gasto Público, Financiamiento y Desincorporación (CIGFD), which determines the relationship for their inclusion in the PEF. The CIGFD prioritizes such projects based on i) socioeconomic profitability; ii) reduction of extreme poverty; iii) regional development; and iv) concurrence with other investment programs and projects.
Authorization
Projects requiring federal funds are authorized by the Chamber of Deputies.
The Investment Unit (UI) will issue an economic feasibility report for those projects that do not require public resources.
Promotion
Under the responsibility of the Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency through the National Coordination of Digital Infrastructure.
Bidding
Under the responsibility of the Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency
Financing
There are several sources of financing depending on the particular characteristics and financial structuring of each project, such as: PEF, National Bank of Public Works and Services (BANOBRAS), National Bank of Foreign Trade (BANCOMEXT), commercial banks, developers and institutional and private investors.
Execution and Operation
The project developers are responsible for its proper execution and operation under the supervision of the Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency.
Projects
Information on new projects (pre-investment, bidding and execution) and in operation within the Mexico Projects Hub platform, which at some stage of the project were considered investment opportunities and do not necessarily have Banobras / Fonadin participation.
New Projects
| Project | Sector | Subsector | Stage | Sustainability | With Ally Networks |
| 0940 Land Complementary Service of the Mobile Satellite Service | Telecommunications | Telecommunications Network | Bidding | No | No |
Projects in Operation
| Project | Sector | Subsector | Stage | Sustainability | With Ally Networks |
| 0369 Public Shared Telecommunications Network | Telecommunications | Telecommunications Network | Operation | Yes | Yes |
| Project | Sector | Subsector | Stage | Sustainability | With Ally Networks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0940 Land Complementary Service of the Mobile Satellite Service | Telecommunications | Telecommunications Network | Execution | Yes | No |
| Project | Sector | Subsector | Stage | Sustainability | With Ally Networks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0369 Public Shared Telecommunications Network | Telecommunications | Telecommunications Network | Operation | Yes | Yes |
Banobras / Fonadin
Project Finance: In order to support the financing of infrastructure projects and public services, the Project Finance Unit structures financing supported by the granting of loans and guarantees to those projects developed as Public-Private Partnerships and which have their own source of payment from the exploitation of the concession or public contract or from the collection of the service in question. The Public-Private Partnership schemes may be Federal and/or Local, in their different modalities, such as: Concessions, Service Provision Projects (PPS) or Financed Public Works Contracts, among others.- The Platform has more than 600 investment opportunities in all its stages, with visits from more than 180 countries and more than 40,000 users per month.

Financing for States and Municipalities and Decentralized Public Organizations: The products and services we offer are designed to meet the infrastructure needs of states, municipalities and their decentralized public organizations, in order to improve the quality of life of the population and increase competitiveness.
Infrastructure is a pillar of development, which is why Banobras has innovative products and services focused on contributing to regional development through the promotion of financial mechanisms to:
Boost investment in infrastructure and public services.
Promote the financial and institutional strengthening of states, municipalities and decentralized public agencies.
To this end, Banobras has the following financing schemes:
Products:
Project Development: Banobras offers services aimed at assisting public sector agencies and entities in the development of infrastructure projects.
Financial structuring of the project:
- Elaborate and/or update studies required by the Public-Private Partnerships Law.
- Support in the review of the bidding conditions and contract model.
- Assist in obtaining financing for the project.
- Assist in the registration process of the project in the portfolio of the Investment Unit of the Ministry of Finance and Public Credit (SHCP).
- Assist in dealing with any observations made by the SHCP Investment Unit.
- Support in the financial closing of the project.
The purpose of the Fondo Nacional de Infraestructura (Fonadin) is to serve as the Federal Public Administration’s coordination vehicle for infrastructure investment. It has one of the largest road concession networks in the world and manages the granting of financial support for infrastructure development, mainly in the areas of communications, transportation, water, environment, energy, tourism, urban and strategic and priority areas, supporting the planning, promotion, construction, conservation, operation and transfer of infrastructure projects with social impact and economic or financial profitability.


It has a wide range of products designed to strengthen the financial structure of the infrastructure projects that the country requires, from the conception to the completion of the projects, providing the following financial instruments that make the projects more attractive for financing with private resources:
Recoverable Support
- Simple Credits
- Subordinated Credits
- Guarantees
- Investments in Venture Capital Funds
- Infrastructure Trust Investments
- Financing of Studies and Advisory Services
Non Recoverable Support
- Contributions for Studies and Consultancy
- Contributions for Projects
- Project Grants
Contact: fonadin@banobras.gob.mx
Sustainability
Banobras makes available to interested parties, analysis sheets for the detection of sustainability practices in infrastructure projects, in accordance with the methodological framework “Attributes and Framework for Sustainable Infrastructure” of the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB). Its objective is to highlight sustainable practices, encourage their adoption in future projects and provide relevant information for investors in their economic, environmental, social and institutional dimensions.
To review the projects that already have a sustainability record, select the “SEARCH CRITERIA>” option in the PROJECTS section, and then select “With sustainability record” at the end of the criteria; the projects that have a record will be displayed below.
In addition, Banobras offers an analysis tool that presents the potential relationship of the different infrastructure projects of the Mexico Projects platform with the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the 2030 Agenda and their targets. This comparative analysis facilitates the use of data according to different criteria, such as the potential impact of projects and sectors against national and global development goals.
The comparison is only made between projects in the same subsector. To select and consult here.
The alignment of a project with the SDGs provides information on the degree of focus on sustainability; it provides a comparison between projects in the same sector and sub-sector and facilitates investment decisions, showing the highest and lowest alignment of projects to the SDGs. Comparative analysis facilitates the use of data according to different criteria, such as the potential impact of projects and sectors against national and global development goals.
In the case of the sector, 1 project is identified in the platform that have sustainability practices detection sheets, which allows to know, among other things, the projects with more and better alignments to the SDGs. For more information, access the Sustainable Development Goals application:

Greater alignment of the sector:
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- SDG 11: Sustainable cities and communities
- SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
Lower alignment of the sector:
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- SDG 14: Life Below Water
- SDG 17: Partnerships
Ally Networks
Banobras, through its Ally Networks application, provides information on companies participating in competitive public procurement processes for infrastructure projects in Mexico, based on official sources such as ComprasMX. It includes details on investment amounts, number of participations in bids, projects awarded, consortiums, and business associations, which allows the user to identify potential actors for the establishment of investments in the country.
To consult the projects that have information on the participating companies, select the option “SEARCH CRITERIA>” in the PROJECTS section, and then select “With applicant companies” at the end of the criteria.
In the application, you can consult on the sector:
- 1 project
- 11 companies
- 2 consortiums
- 1 Projects
- 11 Companies
- 2 Consortiums
Reference documents:
This section offers documents, reports and reports with technical, statistical and regulatory information on the sector:
Official statements:
2025
- 12/17/2025 DOF: DOF: AGREEMENT issuing the General Cybersecurity Policy for the Federal Public Administration
- 11/25/2025 DOF: DECREE issuing the Internal Regulations of the Telecommunications Regulatory Commission
- 11/19/2025 PRESIDENCY: President Claudia Sheinbaum presents the National Cluster and the Mexican Supercomputing Center to position Mexico as a scientific powerhouse
- 10/16/2025 DOF: AGREEMENT approving the Institutional Program of the Telecommunications Investment Promotion Agency 2025–2030
- 09/19/2025 DOF: Sectoral Program of the Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency 2025–2030
- 07/16/2025 DOF: DECREE issuing the Law on Telecommunications and Broadcasting and repealing the Federal Telecommunications and Broadcasting Law
- 05/14/2025 Presidency of the Republic: The new Telecommunications and Broadcasting Law aims to connect 15 million Mexicans without internet access
- 04/21/2025 Government of Mexico: President submits to Congress the National Law to Eliminate Bureaucratic Procedures, facilitating the country’s digital transformation
- 03/13/2025 ATDT: President Claudia Sheinbaum reports the reduction of federal procedures from 342 to 151; to be published in the DOF
- 01/24/2025 DOF: DECREE issuing the Internal Regulations of the Digital Transformation and Telecommunications Agency
2024
- 12/20/2024 DOF: Decree amending, adding, and repealing various provisions of the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States regarding organizational simplification.
- 11/28/2024 DOF: Decree amending, adding, and repealing various provisions of the Organic Law of the Federal Public Administration.
- 09/18/2024 DOF: AGREEMENT by which the Plenary of the Federal Telecommunications Institute modifies various provisions of the Guidelines for the submission, registration, and consultation of information for the formation of the 2024 National Infrastructure Information System.
Additional information:
2024
- IFT: Telecommunications Services Forecast 2023-2024.
- PROMTEL: 2023-2024 Progress and Results Report of PROMTEL’s Institutional Program.
- PROFECO: What I Need to Know About Telecommunications Services.
- IFT: Practical Guide for the Deployment of Telecommunications Infrastructure 2024.
- SICT: Progress and Results (January 2023 – June 2024) of the Communications and Transport Sector Program.
- SICT: Sixth Activity Report 2023-2024.