Financing
In Mexico, many long term sources of funds, in different currencies, are available to finance the development of infrastructure projects: federal funds, the National Infrastructure Fund (FONADIN), development banks, commercial banks, and a wide variety of investment vehicles listed in the stock exchange. Likewise, in recent years many multilateral development organizations, like the Inter-American Development Bank (BID), the International Financial Corporation (IFC), among others, have provided financing for the development of infrastructure in Mexico, based on sustainable and comprehensive projects that provide wellbeing to society.
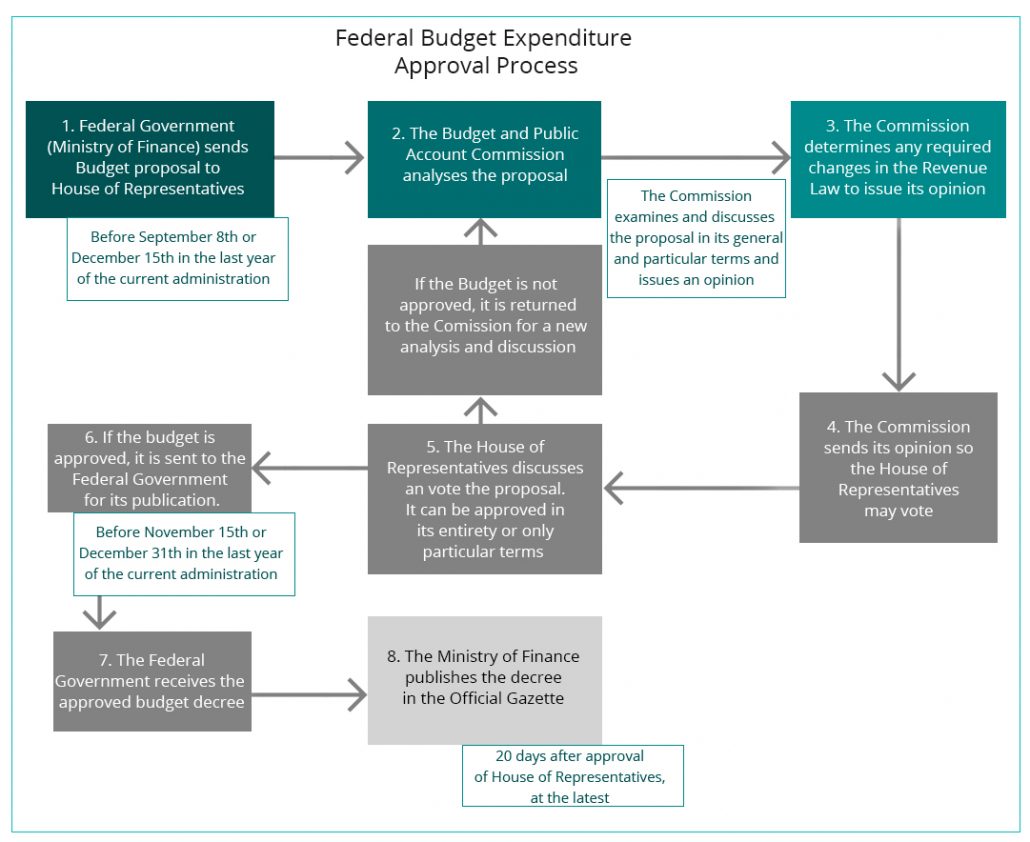
Federal Expenditure Budget (PEF)
The Federal Expenditure Budget is prepared by the Ministry of Finance, and is one of the most important public finances documents. The PEF defines the amount, distribution and destination of public resources to the three powers of government, to autonomous organizations, and transferences to state and municipal governments.
Budget approval is a joint effort between the Federal Government (Ministry of Finance), and the legislative power through the House of Representatives (Budget and Public Account Commission). The Commission analyses the budget proposed by the Ministry of Finance, and issues an opinion for the House of Representatives to vote. If approved, it is returned to the Federal Government for its publication in the Official Gazette. In case of rejection, the proposal is sent back to the Commission for new assessment and discussion. It is important to mention that within this process there are specific terms to comply with.

Development Banks
Mexico has a solid development bank system, consolidated recently as an important long term financier of infrastructure and energy projects , thus benefiting the Mexican economy. Development banks complement commercial banks funds with tailor made financial products, according to the specific needs of each project.
Banobras
Banco Nacional de Obras y Servicios Públicos (BANOBRAS) is a development bank that makes the development of infrastructure projects with high social profitability possible, by providing long term funding to private developers, and state and municipal governments, and by promoting the participation of the private sector and commercial banks. The principal sectors that receive BANOBRAS financing are:
- Communications and transport (roads, ports, airports, railways, telecomm, federal auto transport, etc.)
- Energy
- Water (treatment plants, aqueducts, etc.)
- Solid Waste
- Social Infrastructure
- Urban Infrastructure
Bancomext
Banco Nacional de Comercio Exterior, S.N.C. (BANCOMEXT) is responsible for providing trade finance through loans and guarantees, directly or through financial intermediaries (commercial Banks and other financial institutions) to increase Mexican companies’ productivity and competitiveness. BANCOMEXT offers working capital, project finance, and equipment financing, basically to the following sectors:
- Power
- Industrial parks
- Mining-Metallurgy
- Telecomm
- Transport and logistics
- Tourism
Similarly, it supports different infrastructure sectors such as: power, industrial infrastructure development and tourism infrastructure.
Nafin
Nacional Financiera (NAFIN) contributes to the economic development of the country by facilitating access to small and medium enterprises, entrepreneurs and high priority investment projects, to funding and other corporate development services. Additionally, NAFIN fosters financial markets formation, acting as trustee and financial agent of the Federal Government.
National Infrastructure Fund (FONADIN)
FONADIN is the National Infrastructure Fund that supports the development of communications, transport, water, environmental and tourism sectors by providing grants, venture capital, subordinated debt, credit and guarantees for the design and execution of high impact infrastructure projects.
FONADIN’s principal objectives are to:
- Support the implementation of the National Infrastructure Program.
- Foster private capital flows to infrastructure projects.
- Encourage the participation of the public, private and social sectors in infrastructure development.
- Assume risks that the market is not willing to take.
- Create bankable projects with social or low economic profitability.
- Provide long term financing with competitive conditions.
In addition, FONADIN is concessionaire of a network of more than 50 toll highways, whose revenue allows this fund to finance the development of new infrastructure.

Multilateral Development Banks
The financial support of multilateral organizations such as the Inter-American Development Bank (BID), International Finance Corporation (IFC), and the World Bank (BM) has been crucial in the execution of social projects in the water and sanitation, education, health, power, transport and urban development sectors.
IADB
The Inter-American Development Bank (IADB) was created to finance viable projects for economic, social and institutional development, and to promote a regional trade integration of the Latin American and the Caribbean regions. One of its objectives is to reduce the poverty gap by providing financing to infrastructure projects and technical assistance for the consolidation of its member nations.
IDB Invest
As part of its mission, BID Invest supports the private sector and state-owned enterprises through financing in the form of loans, equity investments, and guarantees. BID Invest also partners with clients to provide advisory and training services.
IFC
IFC is member of the World Bank Group, and is the largest development institution focused exclusively on supporting the private sector in developing countries. IFC has a wide experience in PPP projects, and provides technical assistance and training to governments for the development of effective policies and successful models.
CAF
CAF is committed to the sustained development and regional integration by providing financing to private and public sector customers located in member countries. It is a competitive financial institution, client oriented, sensitive to social needs and backed by highly specialized personnel.
NADBANK
The North American Development Bank was established by the governments of Mexico and the United States in a joint effort aimed at conserving and improving the environmental conditions and quality of life of the people residing along the border between the two countries. NADBANK works with municipal governments and other project developers to support them in the implementation of sound business and financial processes to establish a solid foundation for debt financing. As part of this strategy, NADBANK promotes comprehensive and long-term planning of environmental infrastructure and its financing, as well as offers technical assistance to strengthen the institutional capacities of the entities and support the development of sustainable infrastructure.
World Bank
World Bank provides credits, and grants to developing countries to support a wide array of investments in such areas as education, health, public administration, infrastructure, financial and private sector development, agriculture, and environmental and natural resource management. Some of the projects are cofinanced with governments, other multilateral institutions, commercial banks, export credit agencies, and private sector investors.
European Investment Bank
The EIB is the European Union’s bank. Owned by the EU Member States, it is the world’s largest multilateral borrower and lender. In 2017, the EIB Group provided nearly EUR 80 billion for sound and sustainable investment projects in Europe and beyond. The EIB is headquartered in Luxembourg and has a network of some 40 local offices.
Commercial Banks
Within the Mexican banking system there are international banks that operate worldwide, consolidated national banks and emerging banks. One of the strengths of the Mexican commercial banking system is the soundness of its financial indexes, since the banks comply with the requirements issued by Basel III. Likewise, Mexico has regulatory entities like the National Banking and Securities Commission (Comisión Nacional Bancaria y de Valores or CNBV), the National Commission for the Protection and Defense of the Users of Financial Services (Comisión Nacional para la Protección y Defensa de los Usuarios de Servicios Financieros or Condusef), the Institute for the Protection of Bank Savings (Instituto para la Protección del Ahorro Bancario or IPAB), the Ministry of Finance, and the central bank, Banco de México.
Commercial banks have participated actively in the financing of important infrastructure projects, offering tailor made transactions according to the specific needs of each project; some of these banks have infrastructure areas specialized in roads, airports and ports. Commercial banks offer financing according to the needs of each client and project, varying in amounts, terms and rates, which is reflected in an attractive credit offer for investors and developers.
Investment Vehicles
Mexico has a mature capital market. In the case of infrastructure financing, the private sector and institutional investors can diversify their debt and equity portfolios that include CEBURES (stock exchange certificates), FIBRA (real estate trusts), CKD’s (development capital certificates), and private equity funds. Some of these vehicles are allowed to invest during the different stages of the projects. In 2015, the Federal Government launched two new types of vehicles: FIBRA E (energy and infrastructure) and CERPI’s (investment projects certificates).
A large number of projects have been financed through these vehicles, which are listed in the Mexican Stock Exchange.
Depending on the particular characteristics of these vehicles, some of them specialize in brownfield financing (FIBRA and FIBRA E), while others finance principally greenfield projects (CKD’s and CERPI’s).
For more information on current investment vehicles, please refer to the section Listed Vehicles
FIBRA
FIBRA’s are trust certificates generally documented as fiduciary stock certificates, and are designed to invest in real estate. Its yield (totally or partially) is linked to assets placed in a trust, and the investors have a right over the income generated by such assets. Additional features of these instruments are:
- There is no obligation to pay principal or interests.
- The cash flows are variable and uncertain, linked to the after tax profit generated by the rent / lease of the assets.
- There is a transfer of ownership of the assets or their rights thereof to a trust.
- At least 70% of the assets must be invested in real estate that generates rents.
- The certificates should be listed as equity instruments in a stock exchange.
- The trust does not have a credit risk rating.
- FIBRA’s must comply with the requirements of disclosure and corporate governance that are established in the applicable provisions.
CKD
CKD’s are trust certificates generally documented as fiduciary stock certificates, and are used to finance one or several projects, or one or more companies. Its yield (totally or partially) is linked to the income generated by underlying assets placed in a trust, and to the sale of such assets. Additional features of these instruments are:
- There is no obligation to pay principal or interests.
- The cash flows are variable and uncertain, linked to promoted companies or financed projects.
- CKD’s have a fixed term or expiration date.
- There is a transfer of ownership of the assets or their rights thereof to a trust.
- Disbursements should be done according to a detailed schedule and must be compatible with the development of the financed projects or business plan of the promoted company.
- The certificates should be listed as equity instruments in the Mexican Stock Exchange or in the Bolsa Institucional de Valores.
- The trust does not have a credit risk rating.
- CKD’s must comply with disclosure requirements and corporate governance that are established in applicable provisions
CERPI
CERPI’s are financial instruments with characteristics of corporate governance and design similar to those of private equity funds, which can invest in any economic sector, and receive funding from domestic and foreign investors.
Funds can be received through two vehicles:
- CerPI, which is a listed vehicle in the stock exchange that issues certificates through a restricted public offering, in which only institutional and qualified investors can participate.
- A co-investment fund in which investors other than pension funds may participate.
FIBRA E
FIBRA E is a financial vehicle that invests in mature assets in the energy and infrastructure sectors. The funds are used to develop new projects. This investment vehicle is a derived from the FIBRA’s and the master limited partnerships.


